The steps to create a microcontroller application that functions as an USB Host are:
- Select RTE Components that are required for your application.
- Enable and configure the USB Host Driver.
- Configure the USB Host that connects the USB Middleware to the microcontroller USB peripheral.
- Configure the System Resources according to the USB Host component's Resource Requirements.
- Configure the parameters of the attached USB Devices.
- Implement the Application Code using code templates that are provided to support various USB Device Classes.
- Debug you application using the built-in mechanisms of the USB Component.
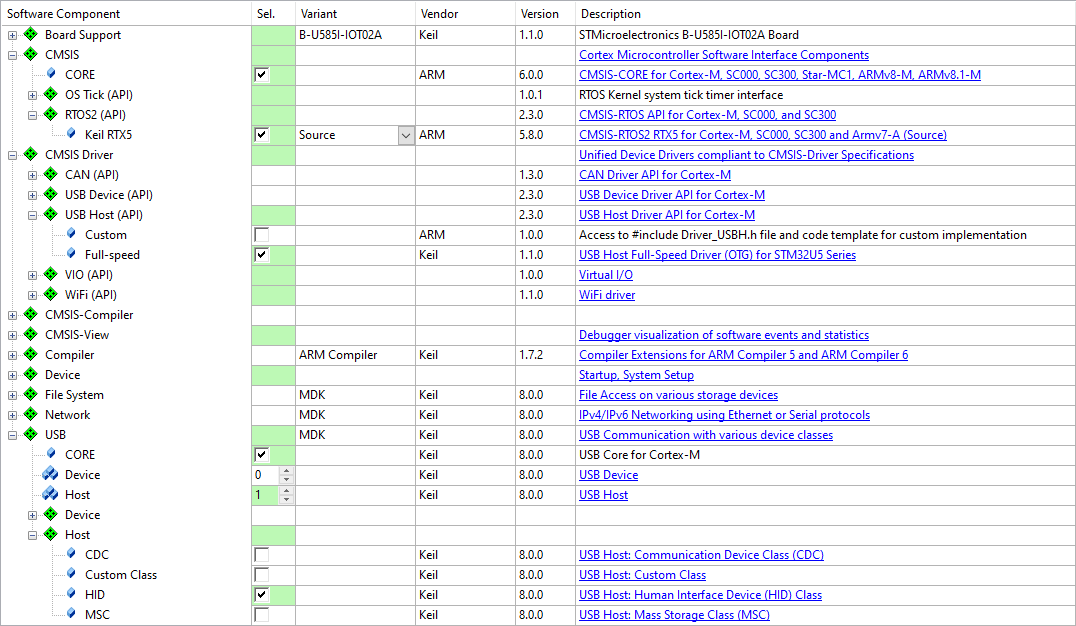
RTE Component Selection
Only a few steps are necessary to complete the RTE Component selection:
- From the USB group:
- Select USB:CORE component that provides the basic functionality required for USB communication.
- Set USB:Host component instances to '1'. This creates one USB Host for communication with the attached USB Devices.
- Select the desired USB Classes (HID/MSC/CDC/Custom Class) components. For example, select USB:Host:HID to support HID Class Devices only.
- From the CMSIS Driver group:
- Select an appropriate USB Host driver component suitable for your microcontroller.
- From the Device group:
- Select the target microcontroller device component.
- Additional device specific driver components may be required according to the validation output.
- From the CMSIS group:
- Select the CMSIS:CORE component to provide the core interface to the processor.
- Select a suitable CMSIS:RTOS2 component that is required by the application.
RTE Component Selection
USB Driver and Controller
The USB Host Driver and the USB Controller of the microcontroller need to be correctly configured. In particular this means:
- The USB Host Driver selected under the Drivers Component is typically configured with a driver specific configuration header file. Some microcontrollers may require settings that related to a physical layer interface (PHY), the USB VBUS power and Overcurrent protection.
- The USB Controller of the microcontroller needs typically specific clock settings. Consult the user's guide of the microcontroller to understand the requirements. Alternatively you may copy the setup of a similar USB Host configuration provided for various evaluation boards (BSP).
USB Host Configuration
The USBH_Config_n.h file contains additional settings for the specific USB Host:
- The Driver_USBH# is set according to the selected USB Controller. For device with single USB Host Controller it will typically be '0'.
- Port Power Delivery can be configured according to hardware capability of the USB Host Controller.
- Maximum Pipes can be specified according to expected USB Device classes that are expected to be used by the USB Host.
- Memory Pool parameters can be configured that are necessary for USB Host operation. This memory pool can also be located to specific memory via the linker script.
Refer to Configuration for a detailed list of all available settings.
System Resource Configuration
For proper operation, the USB Host Component requires some system configuration settings. The requirements are:
- Additional main stack size of 512 bytes.
- The USB Host Component uses CMSIS-RTOS2 threads. In case RTX v5 is used no changes to RTX settings are necessary as all resources are allocated statically.
For more information, check the USB Host component's Resource Requirements section.
Configuration of Attachable USB Devices
In the USBH_Config_HID.h, USBH_Config_MSC.h, USBH_Config_CDC.h, or USBH_Config_CustomClass.h you can specify the number of concurrent USB Devices that the USB Host will support. This has an impact on the amount of memory that will be reserved in your application for the attachment of USB Devices. The Examples shows how to configure an USB Host to interact with different HID, MSC or CDC peripheral devices.
User Code Implementation
files provide function templates to support various USB Device Classes on the USB Host. The available functions are explained in the Reference section of the USB Host Component. These routines can be adapted to the needs of the microcontroller application, in case different then default functionality is needed.
The following templates are available for the USB Host component:
| Template Name | Purpose |
| USBH_MSC.c | Required functions to support MSC devices. The template can be found here. |
| USBH_PL2303.c | Required functions to support the Prolific PL2303 USB to serial RS232 adapter. The template can be found here. |
| USBH_User_CustomClass.c | Required functions to support any USB Device class. The template can be found here. |
Debugging
USB Host Component is distributed in a source form and it allows direct code debug. Also debug events are available (via Event Recorder) which provide non-intrusive debugging during run-time.
USB_Debug.h configuration file is used to configure the level of debug events.
The USB Host:Debug Events describes the events implemented in the USB Device Component.
Event Recorder
is a powerful tool that provides visibility to the dynamic execution of the program.
The USB Host Component generates a broad set of Debug Events for the Event Recorder and implements required infrastructure to interface with it.
To use the Event Recorder it is required to create an image with event generation support. The necessary steps are:
- : in the RTE management dialog enable the software component CMSIS-View:Event Recorder.
- Ensure that Event Recorder is initialized preferably by if CMSIS-RTOS2 RTX v5 is used, or alternatively by calling the function in the application code.
- Event Recorder Configuration: if necessary, adjust default Event Recorder configuration.
- In
USB_Debug.h enable USB Host event generation and configure event filters.
- Build the application code, download it to the target hardware and start debug session.
Now, when the USB Host generates event information, it can be viewed in the .
Configuration
This section describes the configuration settings for the Event Recorder; refer to for more information.
USB Event Generation Configuration
Selecting the USB:CORE will add the file USB_Debug.h to your project. Use this file to set the event generation configuration for USB core, drivers, and device classes separately. The file is common for USB Device and Host components.
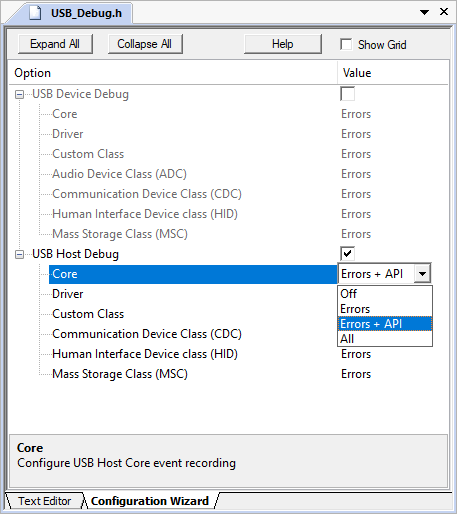
USB_Debug.h file for event generation configuration
The following settings are available for event generation configuration of each module:
- Off means no events will be generated by the module
- Errors means only error events will be generated by the module
- Errors + API means error and API call events will be generated by the module
- All means all available events will be generated by the module. Besides error and API call events, this contains operation and detailed events.
Event IDs
The USB Host component uses the following event IDs:
| Component | Event ID |
| USBH_Core | 0xB0 |
| USBH_Driver | 0xB1 |
| USBH_CC | 0xB2 |
| USBH_CDC | 0xB3 |
| USBH_HID | 0xB4 |
| USBH_MSC | 0xB5 |

