Utilities
The SDS-Framework includes the following utilities that are implemented in Python.
- SDSIO-Server: enables recording and playback of SDS data files via socket (TCP/IP), USB (Bulk transfer) or serial (UART) connection.
- SDS-View: graphical data viewer for SDS data files.
- SDS-Convert: convert SDS data files into CSV, Qeexo V2 CSV, or WAV format.
- SDS-Check: check SDS data files for correctness and consistency.
Requirements
- Python 3.9 or later with packages:
- ifaddr
- matplotlib
- numpy
- pandas
- pyyaml
- pyserial
- libusb1
Setup
Note
- These utilities are located in the SDS-Framework pack installation folder, subfolder
/utilities. Replace2.0.0with the version number of your SDS pack installation.
Perform the following steps to setup the Python environment for using the SDS utilities.
- Install Python or verify the version with:
>python --version
- Navigate in the folder SDS/utilities and install the required Python packages with
pip:
>cd %CMSIS_PACK_ROOT%/ARM/SDS/2.0.0/utilities
>pip install -r requirements.txt
- Add to the system Path environment variable the path to the
%CMSIS_PACK_ROOT%/ARM/SDS/2.0.0/utilitiesfolder.
Notes
%CMSIS_PACK_ROOT%is just a placeholder for the Pack location on your local PC. The Path variable must be extended by the absolute path to theutilitiesfolder.- Do not set the variable
PYTHONPATHas this may conflict with the Python scripts that are used in AVH FVP models. AVH FVP use Python version 3.9 which may create a conflict.
Windows
- On Windows, ensure that the environment variable PATHEXT contains the extension
.PY.
Tip
- When the Path environment variable is configured, you may simply start the utilities by using its name. For example entering
>sdsio-serverstarts the utility.
SDSIO-Server
The Python utility SDSIO-Server enables recording and playback of SDS data files via socket (TCP/IP), USB (Bulk transfer), or serial (UART) connection. It communicates with the target using these SDSIO Client interfaces:
- serial/usart for serial communication via CMSIS-Driver USART.
- socket for TCP/IP communication via IoT Socket using MDK-Middleware, LwIP, or CMSIS-Driver WiFi.
- usb/bulk for communication via USB Bulk transfer using MDK-Middleware.
The SDS data stream is recorded to files with the following naming convention:
<name>.<index>.sds
<name>is the name of the I/O stream specified with the functionsdsRecOpenorsdsPlayOpenon the target.<index>is the zero-based index which is incremented for each subsequent recording.- For more details see Filenames section
The data content of the <name>.<index>.sds is described with metadata file <name>.sds.yml in YAML format.
Usage
- Setup the Python environment.
- Depending on the SDS interface used on the target use either Serial Mode, Socket Mode or USB Mode as described below.
- The SDSIO_Server terminates with
Ctrl+C.
Serial Mode
usage: sdsio-server.py serial [-h]
-p <Serial Port>
[--baudrate <Baudrate>]
[--parity <Parity>]
[--stopbits <Stop bits>]
[--connect-timeout <Timeout>]
[--workdir <Work dir>]
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
required:
-p <Serial Port> Serial port
optional:
--baudrate <Baudrate> Baudrate (default: 115200)
--parity <Parity> Parity: N=None, E=Even, O=Odd, M=Mark, S=Space (default: N)
--stopbits <Stop bits> Stop bits: 1, 1.5, 2 (default: 1)
--connect-timeout <Timeout> Serial port connection timeout in seconds (default: no timeout)
--workdir <Work dir> Directory for SDS files (default: current directory)
Example:
python sdsio-server.py serial -p COM0 --baudrate 115200 --workdir ./work_dir
Socket Mode
usage: sdsio-server.py socket [-h]
[--ipaddr <IP> | --interface <Interface>]
[--port <TCP Port>]
[--workdir <Work dir>]
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
optional:
--ipaddr <IP> Server IP address (cannot be used with --interface)
--interface <Interface> Network interface (cannot be used with --ipaddr)
--port <TCP Port> TCP port (default: 5050)
--workdir <Work dir> Directory for SDS files (default: current directory)
Note
- The
--ipaddrand--interfaceoptions are mutually exclusive. - SDSIO Server only supports IPv4 addresses.
Example:
For Microsoft Windows (using default computer IP):
python sdsio-server.py socket --workdir ./work_dir
For Linux:
python sdsio-server.py socket --interface eth0 --workdir ./work_dir
USB Mode
usage: sdsio-server.py usb [-h]
[--workdir <Work dir>]
[--high-priority]
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
optional:
--workdir <Work dir> Directory for SDS files (default: current directory)
--high-priority Enable high-priority threading for USB server (default: off)
Note
- For more reliable operation at higher data transfer rates, it is recommended to enable the
--high-priorityoption. This increases the thread priority of the SDSIO-Server process. - When using
--high-priority, elevated privileges are required depending on your operating system:- Windows: Run the Python script as an administrator.
- macOS/Linux: Execute the script with
sudoor ensure the user has sufficient permissions.
Example:
python sdsio-server.py usb --workdir ./work_dir
SDS-View
The Python utility SDS-View outputs a time-based plot of SDS data files (<name>.<index>.sds) based on the meta-data file (<name>.sds.yml).
The horizontal time scale is derived from the number of data points in a recording and frequency provided in the metadata description. All plots form a single recording will be displayed on the same figure (shared vertical scale).
If there are 3 values described in the metadata file, an optional 3D view may be displayed.
Limitations
- Data in recording must all be of the same type (float, uint32_t, uint16_t, ...)
Usage
- Setup the Python environment.
- Invoke the tool as explained below.
usage: sds-view.py [-h]
-y <yaml_file>
-s <sds_file> [<sds_file> ...]
[--3D]
View SDS data
options:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
required:
-y <yaml_file> YAML sensor description file
-s <sds_file> [<sds_file> ...] SDS data recording file
optional:
--3D Plot 3D view in addition to normal 2D
Example:
python sds-view.py -y test/Gyroscope.sds.yml -s test/Gyroscope.0.sds
Example display:
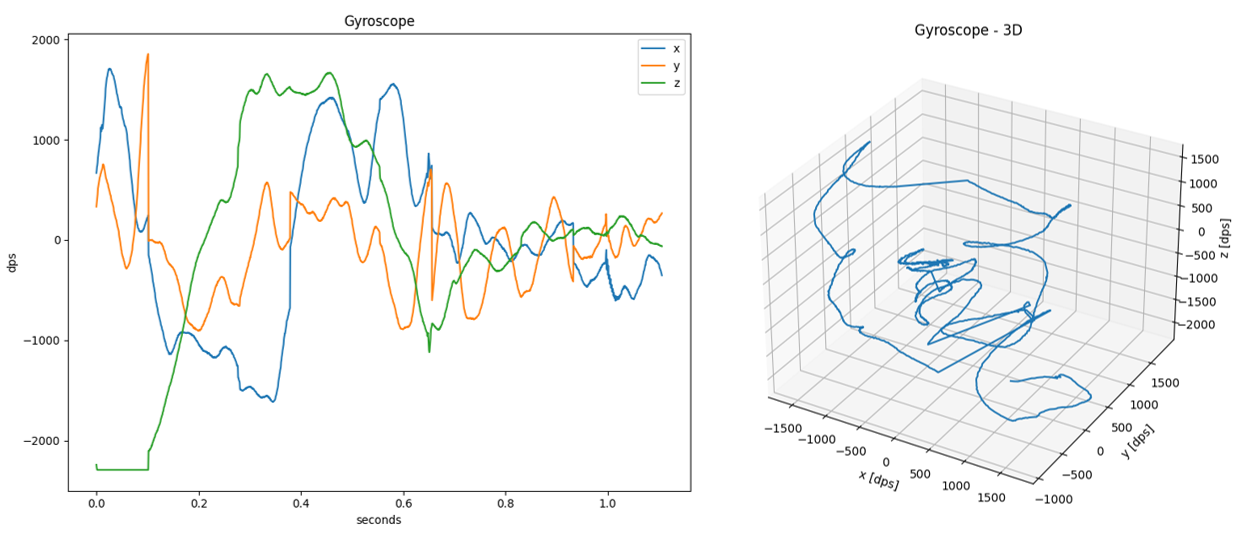
SDS-Convert
The Python utility SDS-Convert converts SDS data files to selected format based on description in metadata (YAML) files.
Usage
- Setup the Python environment.
- Depending on the required format use the tool as shown below.
Audio WAV
The audio_wav mode converts raw microphone data from .sds files into a standard RIFF/WAV file using linear
PCM encoding. The conversion process involves appending a WAV header, generated from parameters specified in the
associated metadata .yml file, to the raw audio data extracted from the .sds stream. The metadata defines
essential audio parameters such as channel configuration (mono or stereo), sample rate (frame rate), and sample
width (bit depth).
usage: sds-convert.py audio_wav [-h]
-i <input_file> [<input_file> ...]
-o <output_file>
[-y <yaml_file> [<yaml_file> ...]]
options:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
required:
-i <input_file> [<input_file> ...] Input file
-o <output_file> Output file
optional:
-y <yaml_file> [<yaml_file> ...] YAML sensor description file
Note
- The metadata and SDS data file pairs must be passed as arguments in the same order to decode the data correctly.
- The tool expects the SDS stream to be strictly audio - no header markers or custom formatting.
Example of metadata yml file for mono microphone:
sds:
name: Microphone
description: Mono microphone with 16kHz sample rate
frequency: 16000
content:
- value: Mono
type: int16_t
Example of metadata yml file for stereo microphone:
sds:
name: Microphone
description: Stereo microphone with 16kHz sample rate
frequency: 16000
content:
- value: Left channel
type: int16_t
- value: Right channel
type: int16_t
Example:
python sds-convert.py audio_wav -i Microphone.0.sds -o microphone.wav -y Microphone.sds.yml
Simple CSV
The simple_csv mode converts sensor data from .sds files into a human-readable CSV format.
This mode is designed for exporting data from a single sensor. If the sensor has multiple
channels, each channel will appear as a separate column in the output CSV.
Timestamps are represented in floating-point format, in seconds. Using the --normalize flag causes
all timestamps in the input file to be offset so that the first timestamp is 0.
Users may specify a time range selection of the input data to be processed using the following flags:
--start-timestamp <timestamp>: Starting input data timestamp in floating-point format, in seconds.--stop-timestamp <timestamp>: Stopping input data timestamp in floating-point format, in seconds.
usage: sds-convert.py simple_csv [-h]
-i <input_file> [<input_file> ...]
-o <output_file>
[-y <yaml_file> [<yaml_file> ...]]
[--normalize]
[--start-timestamp <timestamp>]
[--stop-timestamp <timestamp>]
options:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
required:
-i <input_file> [<input_file> ...] Input file
-o <output_file> Output file
optional:
-y <yaml_file> [<yaml_file> ...] YAML sensor description file
--normalize Normalize timestamps so they start with 0
--start-timestamp <timestamp> Starting input data timestamp, in seconds (default: None)
--stop-timestamp <timestamp> Stopping input data timestamp, in seconds (default: None)
Note
- The metadata and SDS data file pairs must be passed as arguments in the same order to decode the data correctly.
- Current implementation assumes that the tick frequency is
1000 Hzand does not use thetick-frequencyvalue from the metadata file.
Example of metadata yml file for gyroscope:
sds:
name: Gyroscope
description: Gyroscope with 1667Hz sample rate
frequency: 1667
content:
- value: x
type: int16_t
scale: 0.07
unit: dps
- value: y
type: int16_t
scale: 0.07
unit: dps
- value: z
type: int16_t
scale: 0.07
unit: dps
Example:
python sds-convert.py simple_csv -i Gyroscope.0.sds -o gyroscope_simple.csv -y Gyroscope.sds.yml --normalize --start-tick 0.2 --stop-tick 0.3
Qeexo V2 CSV
The qeexo_v2_csv mode converts sensor data from .sds files into a Qeexo V2 CSV format.
Link to Qeexo V2 CSV format specification.
Timestamps are represented in integer format, in milliseconds. Using the --normalize flag causes
all timestamps in the input file to be offset so that the first timestamp is 0.
Users may specify a time range selection of the input data to be processed using the following flags:
--start-timestamp <timestamp>: Starting input data timestamp in integer format, in milliseconds.--stop-timestamp <timestamp>: Stopping input data timestamp in integer format, in milliseconds.
By default, the output file will have raw timestamps in integer format, in milliseconds.
The default output timestamp interval is set to 50 ms.
To override this setting use the --interval <ms> flag, where <ms> is the desired interval in milliseconds.
An optional label can be added to the output by providing a string argument to the --label <text> flag.
This <text> will populate the label column in the output file.
usage: sds-convert.py qeexo_v2_csv [-h] -i <input_file> [<input_file> ...]
-o <output_file>
[-y <yaml_file> [<yaml_file> ...]]
[--normalize]
[--start-timestamp <timestamp>]
[--stop-timestamp <timestamp>]
[--label 'label']
[--interval <interval>]
[--sds_index <sds_index>]
options:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
required:
-i <input_file> [<input_file> ...] Input file
-o <output_file> Output file
optional:
-y <yaml_file> [<yaml_file> ...] YAML sensor description file
--normalize Normalize timestamps so they start with 0
--start-timestamp <timestamp> Starting input data timestamp, in ms (default: None)
--stop-timestamp <timestamp> Stopping input data timestamp, in ms (default: None)
--label 'label' Qeexo class label for sensor data (default: None)
--interval <interval> Qeexo timestamp interval, in ms (default: 50)
--sds_index <sds_index> SDS file index to write (default: <sensor>.0.sds)
Note
- The metadata and SDS data file pairs must be passed as arguments in the same order to decode the data correctly.
- Current implementation assumes that the tick frequency is
1000 Hzand does not use thetick-frequencyvalue from the metadata file.
Example of metadata yml file for accelerometer:
sds:
name: Accelerometer
description: Accelerometer with 1667Hz sample rate
frequency: 1667
content:
- value: x
type: int16_t
scale: 0.000061
unit: G
- value: y
type: int16_t
scale: 0.000061
unit: G
- value: z
type: int16_t
scale: 0.000061
unit: G
Examples:
Convert SDS data files to Qeexo V2 CSV files:
python sds-convert.py qeexo_v2_csv -i Gyroscope.0.sds Accelerometer.0.sds -o sensor_fusion.csv -y Gyroscope.sds.yaml Accelerometer.sds.yaml --normalize --start-tick 200 --stop-tick 300
Convert Qeexo V2 CSV files to SDS data files:
python sds-convert.py qeexo_v2_csv -i accelerometer_data.csv -o accelerometer.sds
SDS-Check
The Python utility SDS-Check checks SDS data files for correctness and consistency.
The following checks are performed:
- Size consistency check: The data size of all records should match the size of the SDS file.
- Timestamp consistency check: Verifies that the timestamps of the records are in ascending order.
- Jitter check: Prints the record with the largest deviation from the average timestamp interval.
- Delta time check: Finds the record with the largest timestamp difference from the following record.
- Duplicate timestamp check: Finds records with identical timestamps.
Usage
- Setup the Python environment.
- Invoke the tool as explained below.
usage: sds-check.py [-h] -s <sds_file> [-t <tick_rate>]
SDS data validation
options:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
required:
-s <sds_file> SDS data recording file
optional:
-t <tick_rate> Timestamp tick rate in Hz (default: 1000 for 1 ms tick interval)
Example:
python sds-check.py -s Accelerometer.0.sds
File Name : Accelerometer.0.sds
File Size : 156.020 bytes
Number of Records : 289
Recording Time : 14 s
Recording Interval: 50 ms
Data Size : 153.748 bytes
Largest Block : 552 bytes
Smallest Block : 462 bytes
Average Block : 532 bytes
Data Rate : 10.640 byte/s
Jitter : Not detected
Validation passed
Note
The default tick frequency is 1000 Hz.
Summary Report
After processing the SDS data file, the SDS-Check utility prints a summary report with statistics:
- File Name : Name of the SDS data file
- File Size : Size of the file in bytes
- Number of Records : Total number of records
- Recording Time : Duration of the recording in seconds or milliseconds
- Recording Interval: Time interval of the recording in milliseconds
- Data Size : Size of the data w/o record headers in bytes
- Largest Block : Largest block size, if different from the average block size
- Smallest Block : Smallest block size, if different from the average block size
- Average Block : Average block size of a data record
- Data Rate : Recorded data rate in bytes per second
- Max Jitter : Maximum deviation from the expected timestamps, if detected (optional)
- Max Delta Time : Largest difference of the neighboring timestamps, if deviating from the recording interval (optional)
- Duplicate Tstamps : Number of duplicated timestamps, if found
Size consistency check
This check processes the SDS data records and calculates the total size of the SDS data. It is the sum of all data records (header + data). This data size should match the size of the SDS file.
If the sizes do not match this error is printed:
Error: File size mismatch. Expected 360 bytes, but file contains 363 bytes.
Timestamp consistency check
This check processes the SDS records and ensures that the timestamps recorded in the records are arranged in ascending order. If the utility detects that the timestamp of the subsequent data record is lower than the current one, this error is printed:
Error: Timestamp not in ascending order in record 23.
Jitter check
This check processes the SDS data records and searches for the maximum deviation of the recorded timestamps from the expected ones. If a deviation is found, the maximum deviation is evaluated as jitter and, together with the record number, is printed in the summary report.
File Name : Gyroscope.0.sds
File Size : 153.334 bytes
Number of Records : 284
Recording Time : 14 s
Recording Interval: 50 ms
Data Size : 151.088 bytes
Largest Block : 606 bytes
Smallest Block : 444 bytes
Average Block : 532 bytes
Data Rate : 10.640 byte/s
Jitter : Not detected
Validation passed
Delta time check
This check processes the SDS records and finds the largest difference in timestamps between two neighboring records, called Max Delta Time.
For normally recorded files, the delta time and the recording interval are identical, so no information about the delta time status is printed. If the delta time and the recording interval are not identical, that is, a difference is detected, the Max Delta Time together with the record number is printed in the summary report.
File Name : Temperature.0.sds
File Size : 360 bytes
Number of Records : 30
Recording Time : 30 s
Recording Interval: 1.024 ms
Data Size : 120 bytes
Data Block : 4 bytes
Data Rate : 4 byte/s
Max Jitter : 59 ms, in record 19
Max Delta Time : 1.050 ms, in record 2
Validation passed
This is not an error, but a report of an anomaly. If the time delta is significantly larger than the sampling interval, for example many times longer, this may indicate that one or more data records are missing from the recorded file.
Duplicate timestamp check
This check processes the SDS records to identify duplicated timestamps. This means that the same timestamp is used in several consecutive data records.
This may indicate that the recording loop in an embedded application is not set up correctly. It is also possible that duplicate timestamps are caused by unexpected thread delays in the embedded application.
Duplicate timestamps are unusual in typical recording files. If multiple timestamps with the same value are found in the SDS file, Duplicate Tstamps will be added to the summary report.
File Name : DataInput.0.sds
File Size : 164.075.008 bytes
Number of Records : 445.856
Recording Time : 446 s
Recording Interval: 1 ms
Data Size : 160.508.160 bytes
Data Block : 360 bytes
Data Rate : 360.000 byte/s
Max Jitter : 26 ms, in record 273.884
Max Delta Time : 35 ms, in record 277.863
Duplicate Tstamps : 4, found at record 1
Validation passed
This is not an error, but a report of an anomaly. The report contains the number of records with the same timestamp and the position in the SDS file where the anomaly was detected (record number).
Note
Only the first occurrence of a duplicate timestamp is reported.