|
| void | arm_fir_decimate_f32 (const arm_fir_decimate_instance_f32 *S, const float32_t *pSrc, float32_t *pDst, uint32_t blockSize) |
| | Processing function for floating-point FIR decimator.
|
| |
| void | arm_fir_decimate_f64 (const arm_fir_decimate_instance_f64 *S, const float64_t *pSrc, float64_t *pDst, uint32_t blockSize) |
| | Processing function for floating-point FIR decimator.
|
| |
| void | arm_fir_decimate_fast_q15 (const arm_fir_decimate_instance_q15 *S, const q15_t *pSrc, q15_t *pDst, uint32_t blockSize) |
| | Processing function for the Q15 FIR decimator (fast variant).
|
| |
| void | arm_fir_decimate_fast_q31 (const arm_fir_decimate_instance_q31 *S, const q31_t *pSrc, q31_t *pDst, uint32_t blockSize) |
| | Processing function for the Q31 FIR decimator (fast variant).
|
| |
| arm_status | arm_fir_decimate_init_f32 (arm_fir_decimate_instance_f32 *S, uint16_t numTaps, uint8_t M, const float32_t *pCoeffs, float32_t *pState, uint32_t blockSize) |
| | Initialization function for the floating-point FIR decimator.
|
| |
| arm_status | arm_fir_decimate_init_f64 (arm_fir_decimate_instance_f64 *S, uint16_t numTaps, uint8_t M, const float64_t *pCoeffs, float64_t *pState, uint32_t blockSize) |
| | Initialization function for the floating-point FIR decimator.
|
| |
| arm_status | arm_fir_decimate_init_q15 (arm_fir_decimate_instance_q15 *S, uint16_t numTaps, uint8_t M, const q15_t *pCoeffs, q15_t *pState, uint32_t blockSize) |
| | Initialization function for the Q15 FIR decimator.
|
| |
| arm_status | arm_fir_decimate_init_q31 (arm_fir_decimate_instance_q31 *S, uint16_t numTaps, uint8_t M, const q31_t *pCoeffs, q31_t *pState, uint32_t blockSize) |
| | Initialization function for the Q31 FIR decimator.
|
| |
| void | arm_fir_decimate_q15 (const arm_fir_decimate_instance_q15 *S, const q15_t *pSrc, q15_t *pDst, uint32_t blockSize) |
| | Processing function for the Q15 FIR decimator.
|
| |
| void | arm_fir_decimate_q31 (const arm_fir_decimate_instance_q31 *S, const q31_t *pSrc, q31_t *pDst, uint32_t blockSize) |
| | Processing function for the Q31 FIR decimator.
|
| |
These functions combine an FIR filter together with a decimator. They are used in multirate systems for reducing the sample rate of a signal without introducing aliasing distortion. Conceptually, the functions are equivalent to the block diagram below:
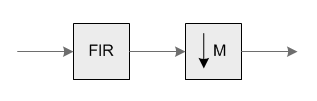
Components included in the FIR Decimator functions
When decimating by a factor of M, the signal should be prefiltered by a lowpass filter with a normalized cutoff frequency of 1/M in order to prevent aliasing distortion. The user of the function is responsible for providing the filter coefficients.
The FIR decimator functions provided in the CMSIS DSP Library combine the FIR filter and the decimator in an efficient manner. Instead of calculating all of the FIR filter outputs and discarding M-1 out of every M, only the samples output by the decimator are computed. The functions operate on blocks of input and output data. pSrc points to an array of blockSize input values and pDst points to an array of blockSize/M output values. In order to have an integer number of output samples blockSize must always be a multiple of the decimation factor M.
The library provides separate functions for Q15, Q31 and floating-point data types.
- Algorithm:
- The FIR portion of the algorithm uses the standard form filter:
y[n] = b[0] * x[n] + b[1] * x[n-1] + b[2] * x[n-2] + ...+ b[numTaps-1] * x[n-numTaps+1]
where, b[n] are the filter coefficients.
- The
pCoeffs points to a coefficient array of size numTaps. Coefficients are stored in time reversed order.
{b[numTaps-1], b[numTaps-2], b[N-2], ..., b[1], b[0]}
pState points to a state array of size numTaps + blockSize - 1. Samples in the state buffer are stored in the order:
{x[n-numTaps+1], x[n-numTaps], x[n-numTaps-1], x[n-numTaps-2]....x[0], x[1], ..., x[blockSize-1]}
The state variables are updated after each block of data is processed, the coefficients are untouched.
- Instance Structure
- The coefficients and state variables for a filter are stored together in an instance data structure. A separate instance structure must be defined for each filter. Coefficient arrays may be shared among several instances while state variable array should be allocated separately. There are separate instance structure declarations for each of the 3 supported data types.
- Initialization Functions
- There is also an associated initialization function for each data type. The initialization function performs the following operations:
- Sets the values of the internal structure fields.
- Zeros out the values in the state buffer.
- Checks to make sure that the size of the input is a multiple of the decimation factor. To do this manually without calling the init function, assign the follow subfields of the instance structure: numTaps, pCoeffs, M (decimation factor), pState. Also set all of the values in pState to zero.
- Use of the initialization function is optional. However, if the initialization function is used, then the instance structure cannot be placed into a const data section. To place an instance structure into a const data section, the instance structure must be manually initialized. The code below statically initializes each of the 3 different data type filter instance structures
arm_fir_decimate_instance_f32 S = {M, numTaps, pCoeffs, pState};
arm_fir_decimate_instance_q31 S = {M, numTaps, pCoeffs, pState};
arm_fir_decimate_instance_q15 S = {M, numTaps, pCoeffs, pState};
where M is the decimation factor; numTaps is the number of filter coefficients in the filter; pCoeffs is the address of the coefficient buffer; pState is the address of the state buffer. Be sure to set the values in the state buffer to zeros when doing static initialization.
- Fixed-Point Behavior
- Care must be taken when using the fixed-point versions of the FIR decimate filter functions. In particular, the overflow and saturation behavior of the accumulator used in each function must be considered. Refer to the function specific documentation below for usage guidelines.
◆ arm_fir_decimate_f32()
Processing function for floating-point FIR decimator.
- Parameters
-
| [in] | S | points to an instance of the floating-point FIR decimator structure |
| [in] | pSrc | points to the block of input data |
| [out] | pDst | points to the block of output data |
| [in] | blockSize | number of input samples to process |
◆ arm_fir_decimate_f64()
Processing function for floating-point FIR decimator.
- Parameters
-
| [in] | S | points to an instance of the floating-point FIR decimator structure |
| [in] | pSrc | points to the block of input data |
| [out] | pDst | points to the block of output data |
| [in] | blockSize | number of input samples to process |
◆ arm_fir_decimate_fast_q15()
Processing function for the Q15 FIR decimator (fast variant).
Processing function for the Q15 FIR decimator (fast variant) for Cortex-M3 and Cortex-M4.
- Parameters
-
| [in] | S | points to an instance of the Q15 FIR decimator structure |
| [in] | pSrc | points to the block of input data |
| [out] | pDst | points to the block of output data |
| [in] | blockSize | number of input samples to process per call |
- Scaling and Overflow Behavior
- This fast version uses a 32-bit accumulator with 2.30 format. The accumulator maintains full precision of the intermediate multiplication results but provides only a single guard bit. Thus, if the accumulator result overflows it wraps around and distorts the result. In order to avoid overflows completely the input signal must be scaled down by log2(numTaps) bits (log2 is read as log to the base 2). The 2.30 accumulator is then truncated to 2.15 format and saturated to yield the 1.15 result.
◆ arm_fir_decimate_fast_q31()
Processing function for the Q31 FIR decimator (fast variant).
Processing function for the Q31 FIR decimator (fast variant) for Cortex-M3 and Cortex-M4.
- Parameters
-
| [in] | S | points to an instance of the Q31 FIR decimator structure |
| [in] | pSrc | points to the block of input data |
| [out] | pDst | points to the block of output data |
| [in] | blockSize | number of samples to process |
- Scaling and Overflow Behavior
- This function is optimized for speed at the expense of fixed-point precision and overflow protection. The result of each 1.31 x 1.31 multiplication is truncated to 2.30 format. These intermediate results are added to a 2.30 accumulator. Finally, the accumulator is saturated and converted to a 1.31 result. The fast version has the same overflow behavior as the standard version and provides less precision since it discards the low 32 bits of each multiplication result. In order to avoid overflows completely the input signal must be scaled down by log2(numTaps) bits (where log2 is read as log to the base 2).
◆ arm_fir_decimate_init_f32()
Initialization function for the floating-point FIR decimator.
- Parameters
-
| [in,out] | S | points to an instance of the floating-point FIR decimator structure |
| [in] | numTaps | number of coefficients in the filter |
| [in] | M | decimation factor |
| [in] | pCoeffs | points to the filter coefficients |
| [in] | pState | points to the state buffer |
| [in] | blockSize | number of input samples to process per call |
- Returns
- execution status
- Details
pCoeffs points to the array of filter coefficients stored in time reversed order:
{b[numTaps-1], b[numTaps-2], b[N-2], ..., b[1], b[0]}
pState points to the array of state variables. pState is of length numTaps+blockSize-1 words where blockSize is the number of input samples passed to arm_fir_decimate_f32(). M is the decimation factor.
◆ arm_fir_decimate_init_f64()
Initialization function for the floating-point FIR decimator.
- Parameters
-
| [in,out] | S | points to an instance of the floating-point FIR decimator structure |
| [in] | numTaps | number of coefficients in the filter |
| [in] | M | decimation factor |
| [in] | pCoeffs | points to the filter coefficients |
| [in] | pState | points to the state buffer |
| [in] | blockSize | number of input samples to process per call |
- Returns
- execution status
- Details
pCoeffs points to the array of filter coefficients stored in time reversed order:
{b[numTaps-1], b[numTaps-2], b[N-2], ..., b[1], b[0]}
pState points to the array of state variables. pState is of length numTaps+blockSize-1 words where blockSize is the number of input samples passed to arm_fir_decimate_f64(). M is the decimation factor.
◆ arm_fir_decimate_init_q15()
Initialization function for the Q15 FIR decimator.
- Parameters
-
| [in,out] | S | points to an instance of the Q15 FIR decimator structure |
| [in] | numTaps | number of coefficients in the filter |
| [in] | M | decimation factor |
| [in] | pCoeffs | points to the filter coefficients |
| [in] | pState | points to the state buffer |
| [in] | blockSize | number of input samples to process |
- Returns
- execution status
- Details
pCoeffs points to the array of filter coefficients stored in time reversed order:
{b[numTaps-1], b[numTaps-2], b[N-2], ..., b[1], b[0]}
pState points to the array of state variables. pState is of length numTaps+blockSize-1 words where blockSize is the number of input samples to the call arm_fir_decimate_q15(). M is the decimation factor.
◆ arm_fir_decimate_init_q31()
Initialization function for the Q31 FIR decimator.
- Parameters
-
| [in,out] | S | points to an instance of the Q31 FIR decimator structure |
| [in] | numTaps | number of coefficients in the filter |
| [in] | M | decimation factor |
| [in] | pCoeffs | points to the filter coefficients |
| [in] | pState | points to the state buffer |
| [in] | blockSize | number of input samples to process |
- Returns
- execution status
- Details
pCoeffs points to the array of filter coefficients stored in time reversed order:
{b[numTaps-1], b[numTaps-2], b[N-2], ..., b[1], b[0]}
pState points to the array of state variables. pState is of length numTaps+blockSize-1 words where blockSize is the number of input samples passed to arm_fir_decimate_q31(). M is the decimation factor.
◆ arm_fir_decimate_q15()
Processing function for the Q15 FIR decimator.
- Parameters
-
| [in] | S | points to an instance of the Q15 FIR decimator structure |
| [in] | pSrc | points to the block of input data |
| [out] | pDst | points to the block of output data |
| [in] | blockSize | number of input samples to process per call |
- Scaling and Overflow Behavior
- The function is implemented using a 64-bit internal accumulator. Both coefficients and state variables are represented in 1.15 format and multiplications yield a 2.30 result. The 2.30 intermediate results are accumulated in a 64-bit accumulator in 34.30 format. There is no risk of internal overflow with this approach and the full precision of intermediate multiplications is preserved. After all additions have been performed, the accumulator is truncated to 34.15 format by discarding low 15 bits. Lastly, the accumulator is saturated to yield a result in 1.15 format.
◆ arm_fir_decimate_q31()
Processing function for the Q31 FIR decimator.
- Parameters
-
| [in] | S | points to an instance of the Q31 FIR decimator structure |
| [in] | pSrc | points to the block of input data |
| [out] | pDst | points to the block of output data |
| [in] | blockSize | number of input samples to process |
- Scaling and Overflow Behavior
- The function is implemented using an internal 64-bit accumulator. The accumulator has a 2.62 format and maintains full precision of the intermediate multiplication results but provides only a single guard bit. Thus, if the accumulator result overflows it wraps around rather than clip. In order to avoid overflows completely the input signal must be scaled down by log2(numTaps) bits (where log2 is read as log to the base 2). After all multiply-accumulates are performed, the 2.62 accumulator is truncated to 1.32 format and then saturated to 1.31 format.
