 |
CMSIS-Zone
Version 1.1.0
System Resource Management
|
 |
CMSIS-Zone
Version 1.1.0
System Resource Management
|
Embedded systems frequently integrate specify hardware for access protection or system isolation. For example, a Cortex-M33 processor based system may incorporate:
Embedded systems may also integrate multiple processors that share system resources (memory and peripherals). In an AMP (Asymmetric Multiprocessor System) it is required to assign or partition the available resources to various processors that execute independent parts of the application software.
CMSIS-Zone helps you to manage this complexity and allows to partition an embedded system into project zones and/or execution zones.
A project zone defines the memory resources and peripherals for a sub-project that execute on the system. Typical examples are boot-loader and user application, however also the secure and non-secure parts of a Cortex-M TrustZone system is defined using project zones.
An execution zone is a software compartment that is protected using a MPU. It defines the access rights to memory and peripherals for a isolated part of the system. This ensures that for example a communication stack (with design flaws) cannot tamper the data or peripherals of other critical parts in a system.
CMSIS-Zone includes a utility that allows you to manage these zones. The input to this utility is a resource (*.rzone) file the defines the system resources including memory and peripherals.
For these resources the user interface of the CMSIS-Zone utility allows:
This system configuration is stored in an assignment (*.azone) file. With the Generate function of the CMSIS-Zone utility, the resource and configuration data can be used to generate:
The following diagram shows the development work flow when using the CMSIS-Zone management tool.
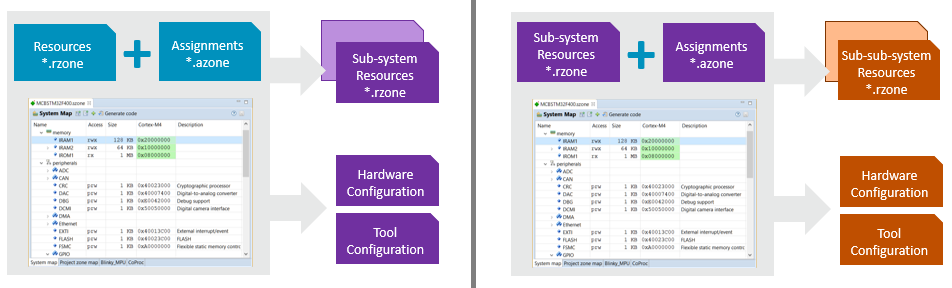
It is possible to uses these steps multiple times which allows to split a complex SoC design with multiple processors into smaller sub-systems. For example a multi-core device can be partitioned in steps:
The following SoC diagram exemplifies step 1 and step 2 of this workflow.
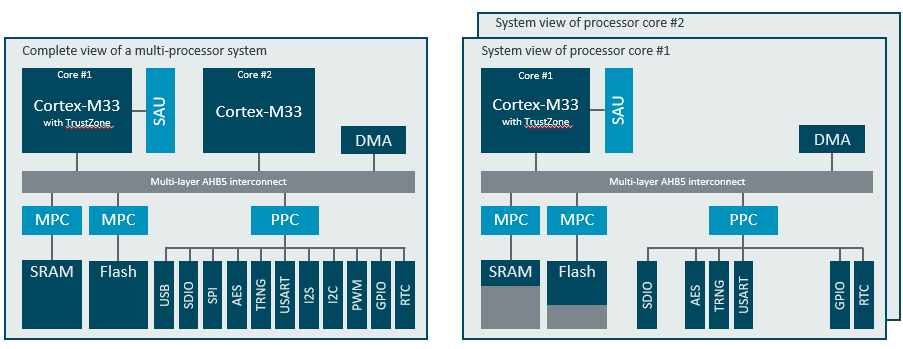
The following sections explain:
This video show how to use the CMSIS-Zone Utility :