Driver API for CAN Bus Peripheral (Driver_CAN.h) More...
Content | |
| CAN Status Error Codes | |
| Status codes of the CAN driver. | |
| CAN Unit Events | |
| Callback unit events notified via ARM_CAN_SignalUnitEvent. | |
| CAN Object Events | |
| Callback objects events notified via ARM_CAN_SignalObjectEvent. | |
| CAN Control Codes | |
| Codes to configure the CAN driver. | |
Data Structures | |
| struct | ARM_DRIVER_CAN |
| Access structure of the CAN Driver. More... | |
| struct | ARM_CAN_CAPABILITIES |
| CAN Device Driver Capabilities. More... | |
| struct | ARM_CAN_STATUS |
| CAN Status. More... | |
| struct | ARM_CAN_MSG_INFO |
| CAN Message Information. More... | |
| struct | ARM_CAN_OBJ_CAPABILITIES |
| CAN Object Capabilities. More... | |
Typedefs | |
| typedef void(* | ARM_CAN_SignalUnitEvent_t) (uint32_t event) |
| Pointer to ARM_CAN_SignalUnitEvent : Signal CAN Unit Event. | |
| typedef void(* | ARM_CAN_SignalObjectEvent_t) (uint32_t obj_idx, uint32_t event) |
| Pointer to ARM_CAN_SignalObjectEvent : Signal CAN Object Event. | |
Functions | |
| ARM_DRIVER_VERSION | ARM_CAN_GetVersion (void) |
| Get driver version. | |
| ARM_CAN_CAPABILITIES | ARM_CAN_GetCapabilities (void) |
| Get driver capabilities. | |
| int32_t | ARM_CAN_Initialize (ARM_CAN_SignalUnitEvent_t cb_unit_event, ARM_CAN_SignalObjectEvent_t cb_object_event) |
| Initialize CAN interface and register signal (callback) functions. | |
| int32_t | ARM_CAN_Uninitialize (void) |
| De-initialize CAN interface. | |
| int32_t | ARM_CAN_PowerControl (ARM_POWER_STATE state) |
| Control CAN interface power. | |
| uint32_t | ARM_CAN_GetClock (void) |
| Retrieve CAN base clock frequency. | |
| int32_t | ARM_CAN_SetBitrate (ARM_CAN_BITRATE_SELECT select, uint32_t bitrate, uint32_t bit_segments) |
| Set bitrate for CAN interface. | |
| int32_t | ARM_CAN_SetMode (ARM_CAN_MODE mode) |
| Set operating mode for CAN interface. | |
| ARM_CAN_OBJ_CAPABILITIES | ARM_CAN_ObjectGetCapabilities (uint32_t obj_idx) |
| Retrieve capabilities of an object. | |
| int32_t | ARM_CAN_ObjectSetFilter (uint32_t obj_idx, ARM_CAN_FILTER_OPERATION operation, uint32_t id, uint32_t arg) |
| Add or remove filter for message reception. | |
| int32_t | ARM_CAN_ObjectConfigure (uint32_t obj_idx, ARM_CAN_OBJ_CONFIG obj_cfg) |
| Configure object. | |
| int32_t | ARM_CAN_MessageSend (uint32_t obj_idx, ARM_CAN_MSG_INFO *msg_info, const uint8_t *data, uint8_t size) |
| Send message on CAN bus. | |
| int32_t | ARM_CAN_MessageRead (uint32_t obj_idx, ARM_CAN_MSG_INFO *msg_info, uint8_t *data, uint8_t size) |
| Read message received on CAN bus. | |
| int32_t | ARM_CAN_Control (uint32_t control, uint32_t arg) |
| Control CAN interface. | |
| ARM_CAN_STATUS | ARM_CAN_GetStatus (void) |
| Get CAN status. | |
| void | ARM_CAN_SignalUnitEvent (uint32_t event) |
| Signal CAN unit event. | |
| void | ARM_CAN_SignalObjectEvent (uint32_t obj_idx, uint32_t event) |
| Signal CAN object event. | |
Driver API for CAN Bus Peripheral (Driver_CAN.h)
The Controller Area Network Interface Bus (CAN) implements a multi-master serial bus for connecting microcontrollers and devices, also known as nodes, to communicate with each other in applications without a host computer. CAN is a message-based protocol, designed originally for automotive applications, but meanwhile used also in many other surroundings. The complexity of the node can range from a simple I/O device up to an embedded computer with a CAN interface and sophisticated software. The node may also be a gateway allowing a standard computer to communicate over a USB or Ethernet port to the devices on a CAN network. Devices are connected to the bus through a host processor, a CAN controller, and a CAN transceiver.
The CAN Driver API allows to implement CAN Interfaces that conform to the
CAN specifications available from BOSCH:
Wikipedia offers more information about the CAN Bus.
CAN 2.0B** Every CAN CMSIS-Driver supports the CAN 2.0B standard
CAN 2.0B supports:
Support for CAN FD depends on the hardware.
A CMSIS-Driver that supports CAN FD has the capability ARM_CAN_CAPABILITIES data field fd_mode = 1, which can be retrieved with the function ARM_CAN_GetCapabilities.
CAN FD supports:
CAN FD does not support Remote Frame requests.
Block Diagram
The CAN Driver API defines a CAN interface for middleware components. The CAN Driver supports multiple nodes, which are able to send and receive messages, but not simultaneously.
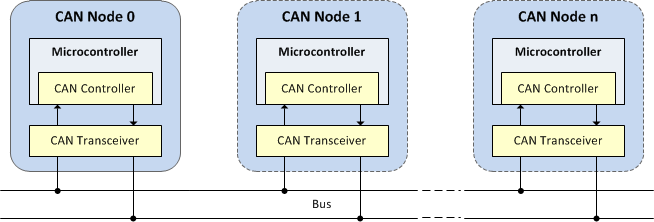
The following header files define the Application Programming Interface (API) for the CAN interface:
The driver implementation is a typical part of the Device Family Pack (DFP) that supports the peripherals of the microcontroller family.
Driver Functions
The driver functions are published in the access struct as explained in Common Driver Functions
Example Code
The following example code shows the usage of the CAN interface.
The CMSIS-Driver for the CAN interface provides multiple CAN message objects, which can be seen as individual communication channels. The number of available CAN message objects depends on the CAN peripheral. The function ARM_CAN_GetCapabilities returns the maximum number of available CAN message objects. The number is encoded in the structure ARM_CAN_CAPABILITIES in the data field num_objects. CAN message objects are addressed with the functions listed below, whereby the parameter obj_idx addresses an individual object. The valid range for obj_idx is [0 .. (num_objects - 1)].
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
| ARM_CAN_ObjectGetCapabilities | Retrieves message object capabilities such as receive, transmit, Remote Frame automatic handling and CAN Message Filtering. |
| ARM_CAN_ObjectSetFilter | Allows to set-up CAN ID filtering for the message object. |
| ARM_CAN_ObjectConfigure | Allows to configure the message object for receive, transmit or Remote Frame automatic handling. |
| ARM_CAN_MessageRead | Read received message from the message object. |
| ARM_CAN_MessageSend | Send CAN message or send Remote Frame or set CAN message to be sent automatically on reception of matching Remote Frame on the message object. |
| ARM_CAN_SignalObjectEvent | Callback function that signals a message transfer or a received message overrun. |
Each CAN message object may have different capabilities. Before using a CAN message object, call the function ARM_CAN_ObjectGetCapabilities to verify the available features.
The CMSIS-Driver for the CAN interface supports ID filtering for the receiving message objects. The receiving CAN node examines the identifier to decide if it was relevant. This filtering is done by the CAN peripheral according the settings configured with the function ARM_CAN_ObjectSetFilter.
The function ARM_CAN_ObjectGetCapabilities retrieves the filter capabilities of the CAN message objects stored in ARM_CAN_OBJ_CAPABILITIES.
| Data Fields | CAN Messages Object can be filtered with ... |
|---|---|
| exact_filtering | an exact ID value set by using the function ARM_CAN_ObjectSetFilter with control = ARM_CAN_FILTER_ID_EXACT_ADD. |
| range_filtering | a range ID value set by using the function ARM_CAN_ObjectSetFilter with control = ARM_CAN_FILTER_ID_RANGE_ADD. |
| mask_filtering | a mask ID value set by as using the function ARM_CAN_ObjectSetFilter with control = ARM_CAN_FILTER_ID_MASKABLE_ADD. |
| multiple_filters | ... several filters to capture multiple ID values, or ID value ranges. |
CAN message filtering using an exact ID
Example: accept in message object #1 only frames with extended ID = 0x1567.
Example: accept in message object #2 frames with extended ID = 0x3167 and extended ID = 0x42123.
CAN message filtering using a range ID
Example: accept in message object #3 only frames with extended ID >= 0x1567 and extended ID <= 0x1577.
CAN message filtering using a mask ID
Using the function ARM_CAN_ObjectSetFilter with control = ARM_CAN_FILTER_ID_MASKABLE_ADD allows to specify with arg a mask value.
Example: accept in message object #0 only frames with extended IDs 0x1560 to 0x156F.
Example: accept in message object #2 only frames with extended IDs 0x35603, 0x35613, 0x35623, and 0x35633.
Example: accept any message in object #4 regardless of the ID.
In general, data transmission is performed on an autonomous basis with the data source node sending out Data Frames.
However, sending a Remote Frame allows a destination node to request the data from the source node. The examples below shows the data exchange using a Remote Transmission Request (RTR).
Example for automatic Data Message response on RTR
For automatic data message response on an RTR, the object is configured with the function ARM_CAN_ObjectConfigure obj_cfg = ARM_CAN_OBJ_RX_RTR_TX_DATA.
In this case, the function ARM_CAN_MessageSend sets a data message that is transmitted when an RTR with a matching CAN ID is received. If ARM_CAN_MessageSend was not called before the RTR is received, the response is hardware dependent (either last data message is repeated or no data message is sent until ARM_CAN_MessageSend is called).
After data transmission is completed, the driver calls a callback function ARM_CAN_SignalObjectEvent with event = ARM_CAN_EVENT_SEND_COMPLETE and the related obj_idx.
Example:
Example for automatic Data Message reception using RTR
For automatic data message reception on an RTR, the object is configured with the function ARM_CAN_ObjectConfigure obj_cfg = ARM_CAN_OBJ_TX_RTR_RX_DATA.
The receiver or consumer requests data with transmission of an RTR with the ARM_CAN_MessageSend. This RTR requests from the transmitter or producer to send the data message. Once the data message is received, the driver calls a callback function ARM_CAN_SignalObjectEvent with event = ARM_CAN_EVENT_RECEIVE and the related obj_idx. The received data message can then be read with the function ARM_CAN_MessageRead.
Example:
| struct ARM_DRIVER_CAN |
Access structure of the CAN Driver.
The functions of the CAN are accessed by function pointers exposed by this structure. Refer to Common Driver Functions for overview information.
Each instance of a CAN provides such an access structure. The instance is identified by a postfix number in the symbol name of the access structure, for example:
A configuration setting in the middleware allows you to connect the middleware to a specific driver instance Driver_CANn.
Data Fields | |
| ARM_DRIVER_VERSION(* | GetVersion )(void) |
| Pointer to ARM_CAN_GetVersion : Get driver version. | |
| ARM_CAN_CAPABILITIES(* | GetCapabilities )(void) |
| Pointer to ARM_CAN_GetCapabilities : Get driver capabilities. | |
| int32_t(* | Initialize )(ARM_CAN_SignalUnitEvent_t cb_unit_event, ARM_CAN_SignalObjectEvent_t cb_object_event) |
| Pointer to ARM_CAN_Initialize : Initialize CAN interface. | |
| int32_t(* | Uninitialize )(void) |
| Pointer to ARM_CAN_Uninitialize : De-initialize CAN interface. | |
| int32_t(* | PowerControl )(ARM_POWER_STATE state) |
| Pointer to ARM_CAN_PowerControl : Control CAN interface power. | |
| uint32_t(* | GetClock )(void) |
| Pointer to ARM_CAN_GetClock : Retrieve CAN base clock frequency. | |
| int32_t(* | SetBitrate )(ARM_CAN_BITRATE_SELECT select, uint32_t bitrate, uint32_t bit_segments) |
| Pointer to ARM_CAN_SetBitrate : Set bitrate for CAN interface. | |
| int32_t(* | SetMode )(ARM_CAN_MODE mode) |
| Pointer to ARM_CAN_SetMode : Set operating mode for CAN interface. | |
| ARM_CAN_OBJ_CAPABILITIES(* | ObjectGetCapabilities )(uint32_t obj_idx) |
| Pointer to ARM_CAN_ObjectGetCapabilities : Retrieve capabilities of an object. | |
| int32_t(* | ObjectSetFilter )(uint32_t obj_idx, ARM_CAN_FILTER_OPERATION operation, uint32_t id, uint32_t arg) |
| Pointer to ARM_CAN_ObjectSetFilter : Add or remove filter for message reception. | |
| int32_t(* | ObjectConfigure )(uint32_t obj_idx, ARM_CAN_OBJ_CONFIG obj_cfg) |
| Pointer to ARM_CAN_ObjectConfigure : Configure object. | |
| int32_t(* | MessageSend )(uint32_t obj_idx, ARM_CAN_MSG_INFO *msg_info, const uint8_t *data, uint8_t size) |
| Pointer to ARM_CAN_MessageSend : Send message on CAN bus. | |
| int32_t(* | MessageRead )(uint32_t obj_idx, ARM_CAN_MSG_INFO *msg_info, uint8_t *data, uint8_t size) |
| Pointer to ARM_CAN_MessageRead : Read message received on CAN bus. | |
| int32_t(* | Control )(uint32_t control, uint32_t arg) |
| Pointer to ARM_CAN_Control : Control CAN interface. | |
| ARM_CAN_STATUS(* | GetStatus )(void) |
| Pointer to ARM_CAN_GetStatus : Get CAN status. | |
| ARM_DRIVER_VERSION(* GetVersion) (void) |
Pointer to ARM_CAN_GetVersion : Get driver version.
| ARM_CAN_CAPABILITIES(* GetCapabilities) (void) |
Pointer to ARM_CAN_GetCapabilities : Get driver capabilities.
| int32_t(* Initialize) (ARM_CAN_SignalUnitEvent_t cb_unit_event, ARM_CAN_SignalObjectEvent_t cb_object_event) |
Pointer to ARM_CAN_Initialize : Initialize CAN interface.
| int32_t(* Uninitialize) (void) |
Pointer to ARM_CAN_Uninitialize : De-initialize CAN interface.
| int32_t(* PowerControl) (ARM_POWER_STATE state) |
Pointer to ARM_CAN_PowerControl : Control CAN interface power.
| uint32_t(* GetClock) (void) |
Pointer to ARM_CAN_GetClock : Retrieve CAN base clock frequency.
| int32_t(* SetBitrate) (ARM_CAN_BITRATE_SELECT select, uint32_t bitrate, uint32_t bit_segments) |
Pointer to ARM_CAN_SetBitrate : Set bitrate for CAN interface.
| int32_t(* SetMode) (ARM_CAN_MODE mode) |
Pointer to ARM_CAN_SetMode : Set operating mode for CAN interface.
| ARM_CAN_OBJ_CAPABILITIES(* ObjectGetCapabilities) (uint32_t obj_idx) |
Pointer to ARM_CAN_ObjectGetCapabilities : Retrieve capabilities of an object.
| int32_t(* ObjectSetFilter) (uint32_t obj_idx, ARM_CAN_FILTER_OPERATION operation, uint32_t id, uint32_t arg) |
Pointer to ARM_CAN_ObjectSetFilter : Add or remove filter for message reception.
| int32_t(* ObjectConfigure) (uint32_t obj_idx, ARM_CAN_OBJ_CONFIG obj_cfg) |
Pointer to ARM_CAN_ObjectConfigure : Configure object.
| int32_t(* MessageSend) (uint32_t obj_idx, ARM_CAN_MSG_INFO *msg_info, const uint8_t *data, uint8_t size) |
Pointer to ARM_CAN_MessageSend : Send message on CAN bus.
| int32_t(* MessageRead) (uint32_t obj_idx, ARM_CAN_MSG_INFO *msg_info, uint8_t *data, uint8_t size) |
Pointer to ARM_CAN_MessageRead : Read message received on CAN bus.
| int32_t(* Control) (uint32_t control, uint32_t arg) |
Pointer to ARM_CAN_Control : Control CAN interface.
| ARM_CAN_STATUS(* GetStatus) (void) |
Pointer to ARM_CAN_GetStatus : Get CAN status.
| struct ARM_CAN_CAPABILITIES |
CAN Device Driver Capabilities.
A CAN driver can be implemented with different capabilities encoded in the data fields of this structure.
Returned by:
| Data Fields | ||
|---|---|---|
| uint32_t | num_objects: 8 | Number of CAN Message Objects available. |
| uint32_t | reentrant_operation: 1 | Support for reentrant calls to ARM_CAN_MessageSend, ARM_CAN_MessageRead, ARM_CAN_ObjectConfigure and abort message sending used by ARM_CAN_Control. |
| uint32_t | fd_mode: 1 | Support for CAN with flexible data-rate mode (CAN_FD) (set by ARM_CAN_Control) |
| uint32_t | restricted_mode: 1 | Support for restricted operation mode (set by ARM_CAN_SetMode) |
| uint32_t | monitor_mode: 1 | Support for bus monitoring mode (set by ARM_CAN_SetMode) |
| uint32_t | internal_loopback: 1 | Support for internal loopback mode (set by ARM_CAN_SetMode) |
| uint32_t | external_loopback: 1 | Support for external loopback mode (set by ARM_CAN_SetMode) |
| uint32_t | reserved: 18 | Reserved (must be zero) |
| struct ARM_CAN_STATUS |
CAN Status.
Structure with information about the status of the CAN unit state and errors. The data fields encode the unit bus state, last error code, transmitter error count, and receiver error count.
Returned by:
| struct ARM_CAN_MSG_INFO |
CAN Message Information.
Structure with information about the CAN message.
In CAN mode, the following ARM_CAN_MSG_INFO data fields are ignored: edl, brs, esi.
In CAN FD mode, the following ARM_CAN_MSG_INFO data field is ignored: rtr.
Parameter for:
| struct ARM_CAN_OBJ_CAPABILITIES |
CAN Object Capabilities.
A CAN object can be implemented with different capabilities encoded in the data fields of this structure.
Returned by:
| ARM_CAN_SignalUnitEvent_t |
Pointer to ARM_CAN_SignalUnitEvent : Signal CAN Unit Event.
Provides the typedef for the callback function ARM_CAN_SignalUnitEvent.
Parameter for:
| ARM_CAN_SignalObjectEvent_t |
Pointer to ARM_CAN_SignalObjectEvent : Signal CAN Object Event.
Provides the typedef for the callback function ARM_CAN_SignalObjectEvent.
Parameter for:
| ARM_DRIVER_VERSION ARM_CAN_GetVersion | ( | void | ) |
Get driver version.
The function ARM_CAN_GetVersion returns version information of the driver implementation in ARM_DRIVER_VERSION
Example:
| ARM_CAN_CAPABILITIES ARM_CAN_GetCapabilities | ( | void | ) |
Get driver capabilities.
The function ARM_CAN_GetCapabilities returns information about the capabilities in this driver implementation. The data fields of the structure ARM_CAN_CAPABILITIES encode various capabilities.
Example:
| int32_t ARM_CAN_Initialize | ( | ARM_CAN_SignalUnitEvent_t | cb_unit_event, |
| ARM_CAN_SignalObjectEvent_t | cb_object_event | ||
| ) |
Initialize CAN interface and register signal (callback) functions.
| [in] | cb_unit_event | Pointer to ARM_CAN_SignalUnitEvent callback function |
| [in] | cb_object_event | Pointer to ARM_CAN_SignalObjectEvent callback function |
The function initializes the CAN interface.
The function performs the following operations:
The parameter cb_unit_event is a pointer to the ARM_CAN_SignalUnitEvent callback function; use a NULL pointer when no callback signals are required.
The parameter cb_object_event is a pointer to the ARM_CAN_SignalObjectEvent callback function; use a NULL pointer when no callback signals are required.
Example:
| int32_t ARM_CAN_Uninitialize | ( | void | ) |
De-initialize CAN interface.
The function ARM_CAN_Uninitialize de-initializes the resources of the CAN interface. It is called to release the software resources used by the interface such as deallocate any RTOS objects, dynamic memory and pin de-configuration.
| int32_t ARM_CAN_PowerControl | ( | ARM_POWER_STATE | state | ) |
Control CAN interface power.
| [in] | state | Power state
|
The function ARM_CAN_PowerControl controls the power modes of the CAN interface.
The parameter state can be:
| uint32_t ARM_CAN_GetClock | ( | void | ) |
Retrieve CAN base clock frequency.
The function ARM_CAN_GetClock returns the CAN base clock frequency in [Hz]. This value may be used to validate the bitrate for the function ARM_CAN_SetBitrate.
Example:
| int32_t ARM_CAN_SetBitrate | ( | ARM_CAN_BITRATE_SELECT | select, |
| uint32_t | bitrate, | ||
| uint32_t | bit_segments | ||
| ) |
Set bitrate for CAN interface.
| [in] | select | Bitrate selection
|
| [in] | bitrate | Bitrate |
| [in] | bit_segments | Bit segments settings
|
The function ARM_CAN_SetBitrate sets the CAN communication bit rate.
The parameter select selects the bit rate affected by function call as defined in ARM_CAN_BITRATE_SELECT and listed in the table below.
| Parameter select | CAN Mode Bit Rate |
|---|---|
| ARM_CAN_BITRATE_NOMINAL | Select nominal (flexible data-rate arbitration) bitrate (CAN 2.0B) |
| ARM_CAN_BITRATE_FD_DATA | Select flexible data-rate data bitrate (CAN_FD) |
The parameter bitrate is the bit rate for the selected CAN mode.
The parameter bit_segments is used to setup the time quanta for sampling (see picture below). The values listed in the table below are ORed and specify the various sampling segments. The CAN controller samples each bit on the bus at the Sample Point.
| Parameter bit_segments | Bit | for select = ARM_CAN_BITRATE_NOMINAL (CAN specification) | for select = ARM_CAN_BITRATE_NOMINAL (CAN FD specification) | for select = ARM_CAN_BITRATE_FD_DATA (CAN FD specification) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ARM_CAN_BIT_PROP_SEG(x) Propagation Time Segment (PROP_SEG) | 0..7 | x = [1..8] | x = [1..32] or more | x = [0..8] |
| ARM_CAN_BIT_PHASE_SEG1(x) Phase Buffer Segment 1 (PHASE_SEG1) | 8..15 | x = [1..8] | x = [1..32] or more | x = [1..8] |
| ARM_CAN_BIT_PHASE_SEG2(x) Phase Buffer Segment 2 (PHASE_SEG2) | 16..23 | x = [1..8] | x = [1..32] or more | x = [1..8] |
| The maximum allowed value is x = MAX (PHASE_SEG1, IPT). IPT = Information Processing Time. Usually, IPT = 2. Exceptions apply. Read the specifications of your CAN controller. | ||||
| ARM_CAN_BIT_SJW(x) (Re-)Synchronization Jump Width (SJW). | 24..31 | x = [1..4] | x = [1..4] | x = [1..4] |
| The maximum allowed value is x = MIN (MIN (PHASE_SEG1, PHASE_SEG2), 4). SJW is not allowed to be greater than either PHASE segment. | ||||
The picture shows a Nominal Bit Time with 10 time quanta.
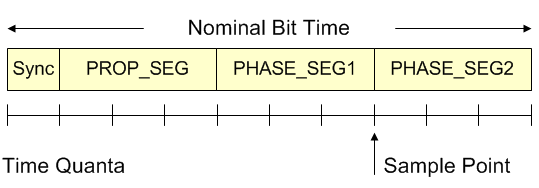
The time quanta (N) per bit is:
The driver uses this value and the CAN clock to calculate a suitable prescaler value (P). If the driver cannot achieve the requested bitrate it returns with ARM_CAN_INVALID_BITRATE. The formula for the bitrate is:
Example:
In this example, N = 8 and with a CAN_Clock = 8MHz the prescaler (P) is calculated by the driver to 8.
| int32_t ARM_CAN_SetMode | ( | ARM_CAN_MODE | mode | ) |
Set operating mode for CAN interface.
| [in] | mode | Operating mode
|
The function ARM_CAN_SetMode sets the CAN bus communication mode using the parameter mode.
The table lists the values for mode.
| Parameter mode | Bus Communication Mode | supported when ARM_CAN_OBJ_CAPABILITIES data field |
|---|---|---|
| ARM_CAN_MODE_INITIALIZATION | Initialization mode; Used to setup communication parameters for the reception objects and global filtering, while peripheral is not active on the bus. Refer to CAN Message Filtering for details. | always supported |
| ARM_CAN_MODE_NORMAL | Normal operation mode. Used when peripheral is in active mode to receive, transmit, and acknowledge messages on the bus. Depending on the current unit state, it can generate error or overload messages. Verify the unit state with ARM_CAN_GetStatus. | always supported |
| ARM_CAN_MODE_RESTRICTED | Restricted operation mode. Used for monitoring the bus communication non-intrusively without transmitting. | restricted_mode = 1 |
| ARM_CAN_MODE_MONITOR | Bus monitoring mode. | monitor_mode = 1 |
| ARM_CAN_MODE_LOOPBACK_INTERNAL | Test mode; loopback of CAN transmission to its receiver. No transmission visible on CAN bus. | internal_loopback = 1 |
| ARM_CAN_MODE_LOOPBACK_EXTERNAL | Test mode; loopback of CAN transmission to its receiver. Transmission is visible on CAN bus. | external_loopback = 1 |
| ARM_CAN_OBJ_CAPABILITIES ARM_CAN_ObjectGetCapabilities | ( | uint32_t | obj_idx | ) |
Retrieve capabilities of an object.
| [in] | obj_idx | Object index |
The function ARM_CAN_ObjectGetCapabilities retrieves the capabilities of a CAN object. The structure ARM_CAN_OBJ_CAPABILITIES stores the values.
The parameter obj_idx is the message object index.
| int32_t ARM_CAN_ObjectSetFilter | ( | uint32_t | obj_idx, |
| ARM_CAN_FILTER_OPERATION | operation, | ||
| uint32_t | id, | ||
| uint32_t | arg | ||
| ) |
Add or remove filter for message reception.
| [in] | obj_idx | Object index of object that filter should be or is assigned to |
| [in] | operation | Operation on filter
|
| [in] | id | ID or start of ID range (depending on filter type) |
| [in] | arg | Mask or end of ID range (depending on filter type) |
The function ARM_CAN_ObjectSetFilter sets or removes the filter for message reception. Refer to CAN Message Filtering for details on filtering.
The parameter obj_idx is the message object index.
The parameter operation is the operation on the filter as listed in the table below and which are defined in the structure ARM_CAN_FILTER_OPERATION.
| Parameter operation | Operation on Filter | supported when ARM_CAN_OBJ_CAPABILITIES data field |
|---|---|---|
| ARM_CAN_FILTER_ID_EXACT_ADD | Add exact ID filter | exact_filtering = 1 |
| ARM_CAN_FILTER_ID_EXACT_REMOVE | Remove exact ID filter | exact_filtering = 1 |
| ARM_CAN_FILTER_ID_RANGE_ADD | Add range ID filter | range_filtering = 1 |
| ARM_CAN_FILTER_ID_RANGE_REMOVE | Remove range ID filter | range_filtering = 1 |
| ARM_CAN_FILTER_ID_MASKABLE_ADD | Add maskable ID filter | mask_filtering = 1 |
| ARM_CAN_FILTER_ID_MASKABLE_REMOVE | Remove maskable ID filter | mask_filtering = 1 |
The parameter id is the identifier of the filter or defines the start of the filter range (depends on the filter operation).
The parameter arg is the mask of the filter or defines the end of the filter range (depends on the filter operation).
| int32_t ARM_CAN_ObjectConfigure | ( | uint32_t | obj_idx, |
| ARM_CAN_OBJ_CONFIG | obj_cfg | ||
| ) |
Configure object.
| [in] | obj_idx | Object index |
| [in] | obj_cfg | Object configuration state
|
The function ARM_CAN_ObjectConfigure configures the message object, which can be a mailbox or FIFO. Refer to CAN Message Filtering for details.
The parameter obj_idx specifies the message object index.
The parameter obj_cfg configures the object with values as shown in the following table.
| Parameter obj_cfg | Object Configuration | supported when ARM_CAN_OBJ_CAPABILITIES data field |
|---|---|---|
| ARM_CAN_OBJ_INACTIVE | Deactivate object (default after ARM_CAN_Initialize) | always supported |
| ARM_CAN_OBJ_RX | Receive object; read received message with ARM_CAN_MessageRead. | rx = 1 |
| ARM_CAN_OBJ_TX | Transmit object; send message with ARM_CAN_MessageSend. | tx = 1 |
| ARM_CAN_OBJ_RX_RTR_TX_DATA | Remote Frame Receive; when RTR is received data message is transmitted; set data message with ARM_CAN_MessageSend. | rx_rtr_tx_data = 1 |
| ARM_CAN_OBJ_TX_RTR_RX_DATA | Remote Frame Transmit; a RTR is sent with ARM_CAN_MessageSend to trigger object reception; read received data message with ARM_CAN_MessageRead. | tx_rtr_rx_data = 1 |
When the object is deactivated, it is not used for data communication.
| int32_t ARM_CAN_MessageSend | ( | uint32_t | obj_idx, |
| ARM_CAN_MSG_INFO * | msg_info, | ||
| const uint8_t * | data, | ||
| uint8_t | size | ||
| ) |
Send message on CAN bus.
| [in] | obj_idx | Object index |
| [in] | msg_info | Pointer to CAN message information |
| [in] | data | Pointer to data buffer |
| [in] | size | Number of data bytes to send |
The function ARM_CAN_MessageSend sends a CAN message on the CAN bus, or sets data message that will be automatically returned upon RTR reception with matching CAN ID.
Only one message can be sent with a call to this function (for CAN up to 8 bytes; for CAN FD up to 64 bytes of data). A message transmission can be terminated with a call to the function ARM_CAN_Control with control = ARM_CAN_ABORT_MESSAGE_SEND.
The parameter obj_idx specifies the message object index.
The parameter msg_info is a pointer to the structure ARM_CAN_MSG_INFO, which contains the following relevant data fields for sending message:
The parameter data is a pointer to the data buffer.
The parameter size is the number of data bytes to send.
The function returns the number of bytes accepted to be sent or ARM_DRIVER_ERROR_BUSY if the hardware is not ready to accept a new message for transmission.
When the message is sent, the callback function ARM_CAN_SignalObjectEvent is called signalling ARM_CAN_EVENT_SEND_COMPLETE on specified object.
Example:
| int32_t ARM_CAN_MessageRead | ( | uint32_t | obj_idx, |
| ARM_CAN_MSG_INFO * | msg_info, | ||
| uint8_t * | data, | ||
| uint8_t | size | ||
| ) |
Read message received on CAN bus.
| [in] | obj_idx | Object index |
| [out] | msg_info | Pointer to read CAN message information |
| [out] | data | Pointer to data buffer for read data |
| [in] | size | Maximum number of data bytes to read |
The function ARM_CAN_MessageRead reads the message received on the CAN bus, if obj_idx was configured for reception or for automatic Data Message reception using RTR and the callback function ARM_CAN_SignalObjectEvent was called signalling ARM_CAN_EVENT_RECEIVE. If the message was overrun by another received message, then the callback function ARM_CAN_SignalObjectEvent will be called signalling ARM_CAN_EVENT_RECEIVE_OVERRUN.
The function can read a maximum of 8 data bytes for CAN and 64 bytes for CAN FD.
The parameter obj_idx specifies the message object index.
The parameter msg_info is a pointer to the CAN information structure.
The parameter data is a pointer to the data buffer for reading data.
The parameter size is data buffer size in bytes and indicates the maximum number of bytes that can be read.
The function returns the number of read data in bytes or the Status Error Codes.
All data fields of the structure ARM_CAN_MSG_INFO are updated as described below:
Message reception can be disabled by de-configuring the receive object with the function ARM_CAN_ObjectConfigure.
| int32_t ARM_CAN_Control | ( | uint32_t | control, |
| uint32_t | arg | ||
| ) |
Control CAN interface.
| [in] | control | Operation
|
| [in] | arg | Argument of operation |
The function ARM_CAN_Control controls the CAN interface settings and executes various operations.
The parameter control specifies various operations that are listed in the table below.
The parameters arg provides, depending on the control value, additional information or set values.
| Parameter control | Operation |
|---|---|
| ARM_CAN_SET_FD_MODE | Select CAN FD mode; arg : 0 = CAN 2.0B; 1 = CAN FD. |
| ARM_CAN_ABORT_MESSAGE_SEND | Abort sending of CAN message; arg : object index |
| ARM_CAN_CONTROL_RETRANSMISSION | Enable/disable automatic retransmission; arg : 0 = disable, 1 = enable (default state) |
| ARM_CAN_SET_TRANSCEIVER_DELAY | Set transceiver delay; arg : delay in time quanta |
Verify the CAN interface capabilities with ARM_CAN_GetCapabilities.
| ARM_CAN_STATUS ARM_CAN_GetStatus | ( | void | ) |
Get CAN status.
The function ARM_CAN_GetStatus retrieves runtime information on CAN bus and CAN unit state.
The following defines give information about the current unit involvement in bus communication:
| Unit State | Description |
|---|---|
| ARM_CAN_UNIT_STATE_INACTIVE | Unit state: Not active on the bus. Unit is in initialization state. |
| ARM_CAN_UNIT_STATE_ACTIVE | Unit state: Active on the bus. Unit can generate active error frames. |
| ARM_CAN_UNIT_STATE_PASSIVE | Unit state: Error passive. Unit is interacting on the bus but does not send active error frames. |
| ARM_CAN_UNIT_STATE_BUS_OFF | Unit state: Bus-off. Unit does not participate on the bus but monitors it and can recover to active state. |
The following defines are error codes of the last error that happened on the bus:
| Last Error Code | Description |
|---|---|
| ARM_CAN_LEC_NO_ERROR | No error. There was no error since last read of status or last successful transmit or receive. |
| ARM_CAN_LEC_BIT_ERROR | Bit error. The bit monitored is different than the bit sent (except during arbitration phase). |
| ARM_CAN_LEC_STUFF_ERROR | Bit stuffing error. There were 6 consecutive same bit levels on the bus. |
| ARM_CAN_LEC_CRC_ERROR | CRC error. CRC of received data is not as expected. |
| ARM_CAN_LEC_FORM_ERROR | Illegal fixed-form bit. Error in fixed form bits. |
| ARM_CAN_LEC_ACK_ERROR | Acknowledgment error. Message was not acknowledged by any receiver on the bus. |
| void ARM_CAN_SignalUnitEvent | ( | uint32_t | event | ) |
Signal CAN unit event.
| [in] | event | CAN Unit Events |
The function ARM_CAN_SignalUnitEvent is a callback function registered by the function ARM_CAN_Initialize.
The parameter event indicates unit event that occurred during driver operation.
The following callback notifications are generated:
| Parameter event | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| ARM_CAN_EVENT_UNIT_INACTIVE | 0 | Unit entered Inactive state. |
| ARM_CAN_EVENT_UNIT_ACTIVE | 1 | Unit entered Error Active state. |
| ARM_CAN_EVENT_UNIT_WARNING | 2 | Unit entered Error Warning state (one or both error counters >= 96). |
| ARM_CAN_EVENT_UNIT_PASSIVE | 3 | Unit entered Error Passive state. |
| ARM_CAN_EVENT_UNIT_BUS_OFF | 4 | Unit entered Bus-off state. |
| void ARM_CAN_SignalObjectEvent | ( | uint32_t | obj_idx, |
| uint32_t | event | ||
| ) |
Signal CAN object event.
| [in] | obj_idx | Object index |
| [in] | event | CAN Object Events |
The function ARM_CAN_SignalObjectEvent is a callback function registered by the function ARM_CAN_Initialize and signals a CAN message object event.
The parameter obj_idx is the index of the message object.
The parameter event indicates object event that occurred during driver operation.
The following events can be generated:
| Parameter event | Bit | Description |
|---|---|---|
| ARM_CAN_EVENT_SEND_COMPLETE | 0 | Message was sent successfully by the obj_idx object. |
| ARM_CAN_EVENT_RECEIVE | 1 | Message was received successfully by the obj_idx object. |
| ARM_CAN_EVENT_RECEIVE_OVERRUN | 2 | Message was overwritten before it was read on the obj_idx object. |