API for Virtual I/O (VIO) (cmsis_vio.h) More...
Content | |
| Signals | |
| Signal related defines. | |
| Value IDs | |
| Value Identifier related defines. | |
Functions | |
| void | vioInit (void) |
| Initialize test input, output. | |
| void | vioSetSignal (uint32_t mask, uint32_t signal) |
| Set signal output. | |
| uint32_t | vioGetSignal (uint32_t mask) |
| Get signal input. | |
| void | vioSetValue (uint32_t id, int32_t value) |
| Set value output. | |
| int32_t | vioGetValue (uint32_t id) |
| Get value input. | |
API for Virtual I/O (VIO) (cmsis_vio.h)
The VIO software component is a virtual I/O abstraction for peripherals that are typically used in example projects. It enables developers to move from an evaluation kit to custom hardware and helps to scale project examples at large to many development boards:
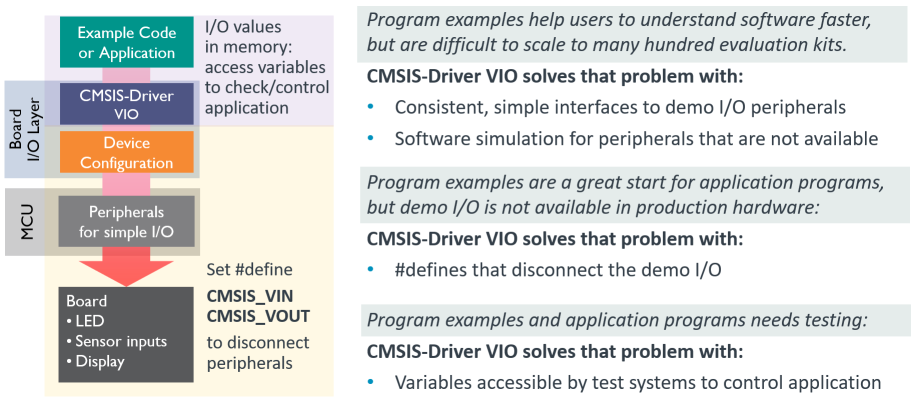
VIO API
The following header file defines the Application Programming Interface (API) for VIO:
VIO User Code Templates
The VIO software component contains two user code templates with different purposes:
VIO Memory Location Structure
For testing purposes, it is required to have fixed memory locations that are used to read/store values. In the VIO:Virtual template file (vio.c), an exemplary implementation is shown:
Use these memory locations to monitor or set the variables as required in the application.
Two defines are available that help to disconnect the actual peripherals and enable virtual I/Os: CMSIS_VIN and CMSIS_VOUT. They help to write code that can be used in testing environments without real hardware access. The following implementation example shows such code:
Code Example (VIO Implementation)
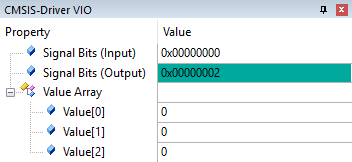
Memory display in IDEs
Arm Keil MDK uses the provided SCVD file to display the VIO signals in Component Viewer:
| void vioInit | ( | void | ) |
Initialize test input, output.
The function vioInit initializes the VIO interface. Use it to initialize any connected hardware that is used to map VIO signals.
Code Example:
| void vioSetSignal | ( | uint32_t | mask, |
| uint32_t | signal | ||
| ) |
Set signal output.
| [in] | mask | bit mask of signals to set. |
| [in] | signal | signal value to set. |
The function vioSetSignal set a signal to an output specified by mask. Use this function to map VIOs to actual hardware for displaying signals on a target board.
Refer to Signals for information about the possible mask and signal values.
Code Example:
| uint32_t vioGetSignal | ( | uint32_t | mask | ) |
Get signal input.
| [in] | mask | bit mask of signals to read. |
The function vioGetSignal retrieves a signal from an input identified by mask. Use this function to read data from any input that is provided.
Refer to Signals for information about the possible mask values.
Code Example:
| void vioSetValue | ( | uint32_t | id, |
| int32_t | value | ||
| ) |
Set value output.
| [in] | id | output identifier. |
| [in] | value | value to set. |
The function vioSetValue set the value to the output identified by id. Use this function to set states of I/Os for example.
Refer to Value IDs for information about id.
Code Example:
| int32_t vioGetValue | ( | uint32_t | id | ) |
Get value input.
| [in] | id | input identifier. |
The function vioGetValue retrieves a value from the input identified by id. Use this function to read data from inputs.
Refer to Value IDs for information about id.
Code Example: