Implement application specific behaviour of a Human Interface Device (HID) Class USB Device.
More...
|
| | User API |
| | User API reference of the Human Interface Device Class.
|
| |
| | Configuration |
| | Configuration of the USB Device HID Class.
|
| |
Implement application specific behaviour of a Human Interface Device (HID) Class USB Device.
The HID class in the USB Component is used for data exchange. It implements a vendor defined HID class with Usage Page ID=0xFF00.
Refer to:
The USB Component allows multiple instances of the HID class. This feature is used to create USB Composite Devices. Each HID class instance has a separate files and interface functions:
- A configuration file USBD_Config_HID_n.h.
- An application-specific user source code file, which can be implemented with the USBD_User_HID_n.h.
- Functions that start with the prefix USBD_HIDn_ are available for each instance of a HID class.
This documentation uses n as a placeholder for the instance number 0 - 3. Most applications only require one instance of a HID class. For the first HID class instance the instance number is 0:
- USBD_Config_HID_0.h
- USBD_User_HID_0.c
- The function prefix is USBD_HID0_
Descriptor Requirements The following descriptors are required in an USB HID Device:
- Standard Device Descriptor
- Standard Configuration Descriptor
- Standard Interface Descriptor for the HID Class
- Class-Specific HID Descriptor
- Standard Endpoint Descriptor for Interrupt IN endpoint
- Class-Specific Report Descriptor
The necessary descriptors are automatically generated by the USB Middleware Component. The report descriptor is built based on the settings in the USBD_Config_HID_x.h file. The number of reports and their maximum size are specified in this file. The page USB Descriptors provides more information on the topic.
Software Structure
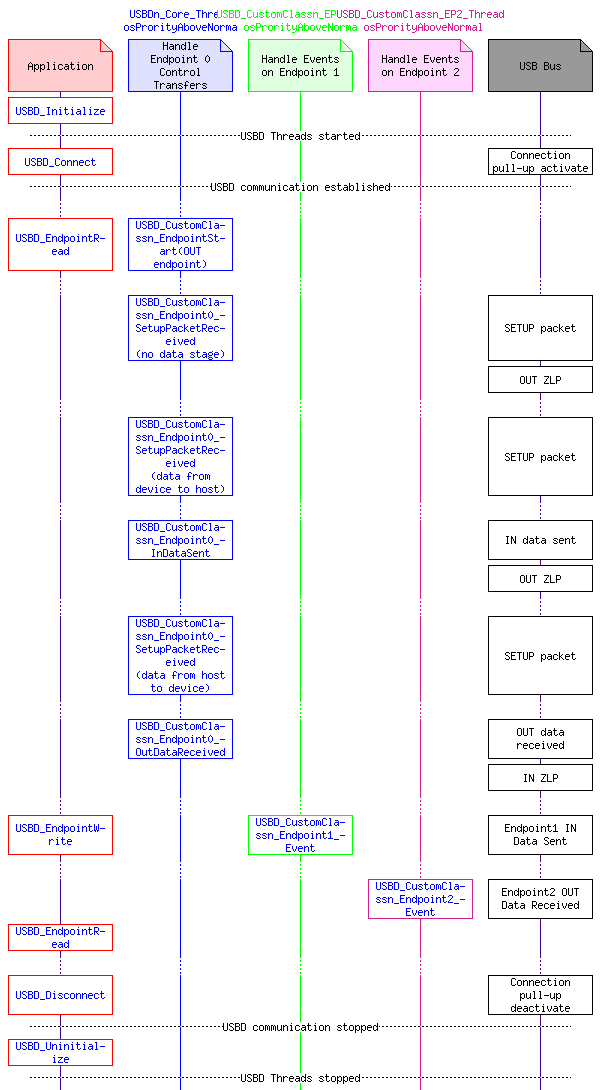
The handling for the HID class endpoint events is implemented in USBD_HIDn_Thread which is started by USBD_Initialize. Each instance of a HID class runs an instance of USBD_HIDn_Thread which calls the data exchange functions USBD_HIDn_GetReport and USBD_HIDn_SetReport.
USBD_HID_GetReportTrigger may be called from any user thread to send asynchronous data reports to the USB Host. USBD_HID_GetReportTrigger cannot be called from interrupt service routines (ISR) as it may wait for previous data to be sent.
The HID class uses a CMSIS-RTOS2 timer set to a 4ms interval to handle polling reports. The polling timing is defined with Endpoint Descriptor. For more information refer to "Set_Idle Request" in Device Class Definition HID specification which is provided by USB Implementers Forum (USB-IF).
Implementation
To create an USB Device with a HID class:
User Code Templates
There are two user code templates available that help to add support for an HID device:
- USBD_User_HID.c contains all the callback functions that need to be implemented by the user.
- USBD_User_HID_Mouse.c is a code template for the application specific functionality of a USB HID Device acting as a mouse pointer input device.
User Code Template USBD_User_HID.c
The following source code can be used to implement the application specific behavior of an USB HID Device.
#include <stdint.h>
void USBD_HID%Instance%_Initialize (void) {
}
void USBD_HID%Instance%_Uninitialize (void) {
}
int32_t USBD_HID%Instance%_GetReport (uint8_t rtype, uint8_t req, uint8_t rid, uint8_t *buf) {
(void)buf;
switch (rtype) {
case HID_REPORT_INPUT:
switch (rid) {
case 0:
switch (req) {
break;
break;
default:
break;
}
break;
default:
break;
}
break;
case HID_REPORT_FEATURE:
break;
default:
break;
}
return 0;
}
bool USBD_HID%Instance%_SetReport (uint8_t rtype, uint8_t req, uint8_t rid, const uint8_t *buf, int32_t len) {
(void)req;
(void)rid;
(void)buf;
(void)len;
switch (rtype) {
case HID_REPORT_OUTPUT:
break;
case HID_REPORT_FEATURE:
break;
default:
break;
}
return true;
}
User Code Template USBD_User_HID_Mouse.c
The following source code can be used to implement the application specific behavior of an USB HID Mouse Device.
#include <stdint.h>
extern
const uint8_t usbd_hid%Instance%_report_descriptor[];
const uint8_t usbd_hid%Instance%_report_descriptor[] = {
HID_UsagePage(HID_USAGE_PAGE_GENERIC),
HID_Usage(HID_USAGE_GENERIC_MOUSE),
HID_Collection(HID_Application),
HID_Usage(HID_USAGE_GENERIC_POINTER),
HID_Collection(HID_Physical),
HID_UsagePage(HID_USAGE_PAGE_BUTTON),
HID_UsageMin(1),
HID_UsageMax(3),
HID_LogicalMin(0),
HID_LogicalMax(1),
HID_ReportCount(3),
HID_ReportSize(1),
HID_Input(HID_Variable),
HID_ReportCount(1),
HID_ReportSize(5),
HID_Input(HID_Constant),
HID_UsagePage(HID_USAGE_PAGE_GENERIC),
HID_Usage(HID_USAGE_GENERIC_X),
HID_Usage(HID_USAGE_GENERIC_Y),
HID_Usage(HID_USAGE_GENERIC_WHEEL),
HID_LogicalMin((uint8_t)(-127)),
HID_LogicalMax(127),
HID_ReportSize(8),
HID_ReportCount(3),
HID_Input(HID_Variable | HID_Relative),
HID_EndCollection,
HID_EndCollection,
};
void USBD_HID%Instance%_Initialize (void) {
}
void USBD_HID%Instance%_Uninitialize (void) {
}
int32_t USBD_HID%Instance%_GetReport (uint8_t rtype, uint8_t req, uint8_t rid, uint8_t *buf) {
(void)buf;
switch (rtype) {
case HID_REPORT_INPUT:
switch (rid) {
case 0:
switch (req) {
break;
break;
default:
break;
}
break;
default:
break;
}
break;
case HID_REPORT_FEATURE:
break;
default:
break;
}
return (0);
}
bool USBD_HID%Instance%_SetReport (uint8_t rtype, uint8_t req, uint8_t rid, const uint8_t *buf, int32_t len) {
(void)req;
(void)rid;
(void)buf;
(void)len;
switch (rtype) {
case HID_REPORT_OUTPUT:
break;
case HID_REPORT_FEATURE:
break;
default:
break;
}
return true;
}