This chapter describes the software structure of the USB Host Component and explains its use for creating an USB Host application.
The USB Host Component simplifies software development of microcontroller systems that can communicate with USB Devices.
Attributes of the USB Host Component:
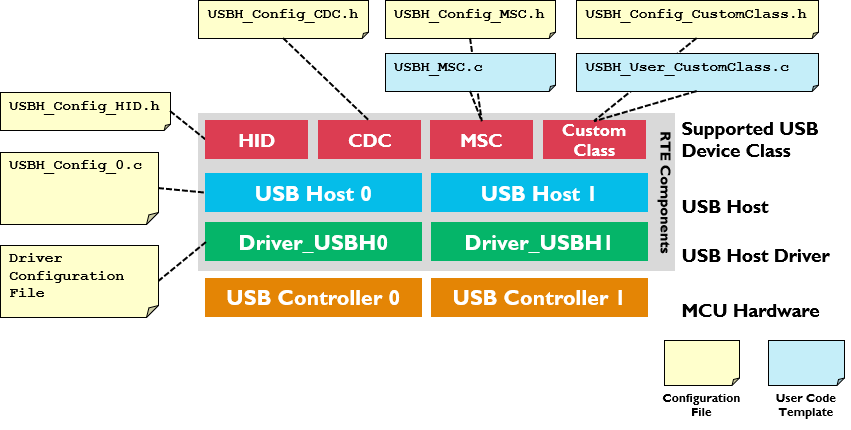
The following picture shows the relationships of the RTE Components with the microcontroller's USB Host peripheral (USB Controller). RTE Components provide configuration files and user code templates.